

Explosion-proof type definition
"E" increased safety type:Additional measures are taken on electrical equipment to improve safety against the possibility of dangerous temperatures, arcing and sparks under normal operation or specified abnormal conditions.
"NA" non-spark device:A device that is structurally designed to minimize the risk of ignition arcs and sparks under normal operating conditions.
From that point of view, it's easy to say,Increased safety type motor can prevent arc and spark in operation, and "nA" type although called no spark but can not completely prevent and eliminate sparks, but to the greatest extent to reduce sparks.The "nA" device keeps the chance of a spark low enough to cause an acceptable risk. Therefore, it is not difficult to understand why the standard stipulates that the partially increased safety type motor (under certain conditions) can reach Gb class, while the sparkless motor can only be Gc class.
Comparison of structure and performance requirements
1. Increased safety motor (using current protection device to prevent exceeding the limit temperature) has requirements on the starting current ratio IA/IN and tE time, and should be marked on the motor nameplate, its purpose is toIt is easy to select and configure suitable protection devices when using the motor, while non-spark motor is not required.
2. Increased safety type and non-spark type motor have requirements for electrical clearance and creepage distance, but at the same voltage level,The minimum electric clearance and minimum creepage distance between live parts of an increased safety motor are required to be larger than that of a non-spark motor(See Table 1 for details), and the material grade of insulating parts used by the non-spark motor can be as low as grade ⅲ B, while the increased safety motor needs to use grade ⅲ A or above.
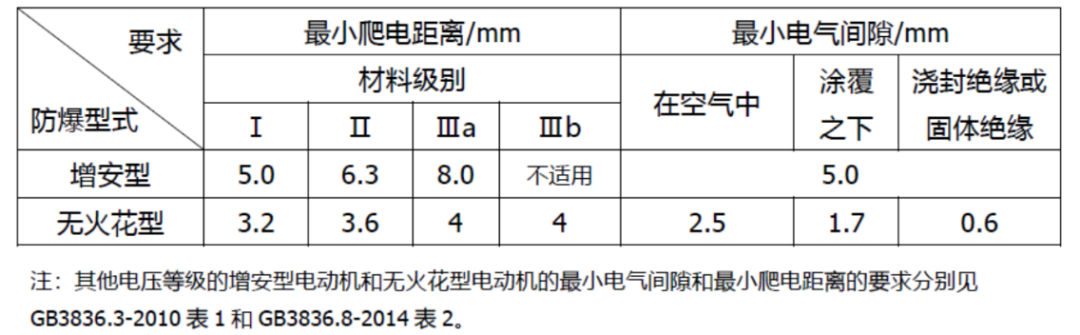
Table 1 Different requirements for creepage distance and electric gap between the increased safety type and the non-spark type when the voltage level is ≤250V
3. For the requirements of squirrel cage rotor, the increased safety type motor should be evaluated according to gb3836.3-2010 Table 4: Potential Air Gap Spark Risk Assessment for squirrel cage Rotor Igniting risk factor, while for sparkless motor, Only the motor with rated output greater than 100kW, except for S1 or S2 working system, shall be assessed according to gb3836.8-2014 Table 6 "Potential Air Gap Spark Risk Assessment of Squirrel cage Rotor Igniting Risk Factor" (see Figure 1 for the difference), and then determine whether additional measures are needed to ensure that the motor will not explode when starting and running.
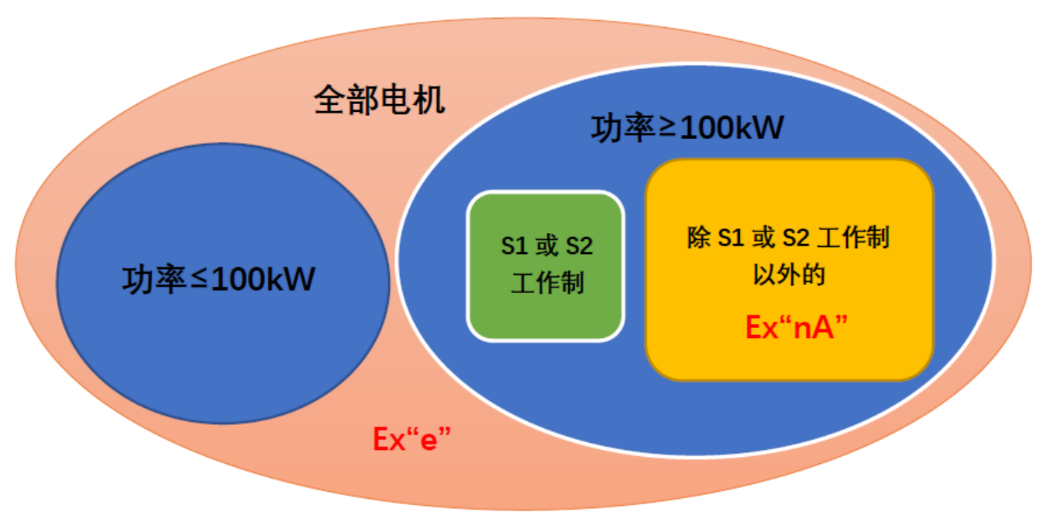
FIG. 1 Scope of motor requiring air gap spark hazard assessment for safety-enhanced type and spark-free type
4. As for the requirements of stator winding insulation system, the increased safety type motor with rated voltage over 1kV should have special protection measures to ensure that there is no explosive gas in its shell when starting, while the non-spark type motor does not have such requirements. It is only recommended to minimize the partial discharge of the high voltage winding. For winding with rated voltage ≥6.6 kV, it is recommended to use materials that can inhibit partial discharge.
Comparison of test requirements